区块链的英文是Blockchain。UnderstandingBlockchain:AComprehensiveGuideIntroduction...
区块链的英文是 Blockchain。
Understanding Blockchain: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to Blockchain

Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary force in the digital age, disrupting various industries and reshaping the way we perceive and interact with data. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to blockchain, covering its basics, working principles, applications, and future prospects.
What is Blockchain?
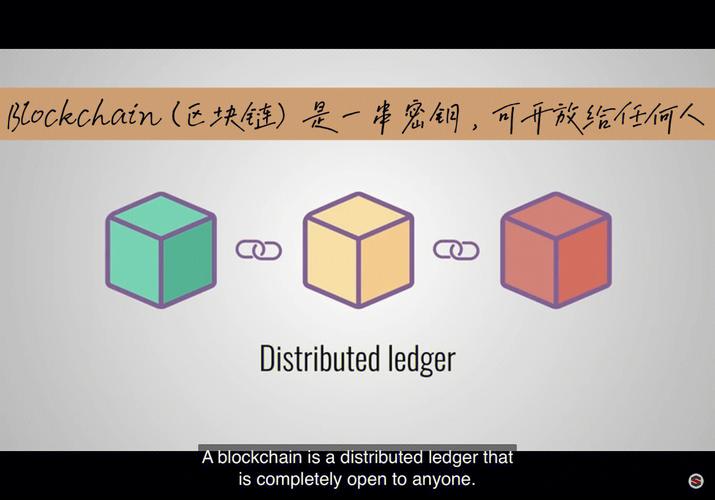
Definition

Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across many computers so that the record cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks and the consensus of the network. It is essentially a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions.
Key Features
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized systems, blockchain operates on a decentralized network, ensuring no single entity has control over the entire system.
- Immutability: Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, providing a high level of security and trust.
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to all participants in the network, fostering transparency and accountability.
- Consensus Mechanism: Blockchain relies on a consensus mechanism to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain.

How Does Blockchain Work?

Transaction Process
1. Transaction Creation: A transaction is created and broadcasted to the network.

2. Validation: Nodes in the network validate the transaction based on predefined rules.
3. Block Formation: Validated transactions are grouped into a block.
4. Mining: Miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to add the block to the blockchain.

5. Consensus: Once a block is added, it is verified by the network, and the process repeats for the next block.
Consensus Mechanisms

- Proof of Work (PoW): Miners compete to solve complex puzzles, and the first to solve it gets to add the block to the blockchain.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Participants are chosen to validate transactions based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to \











